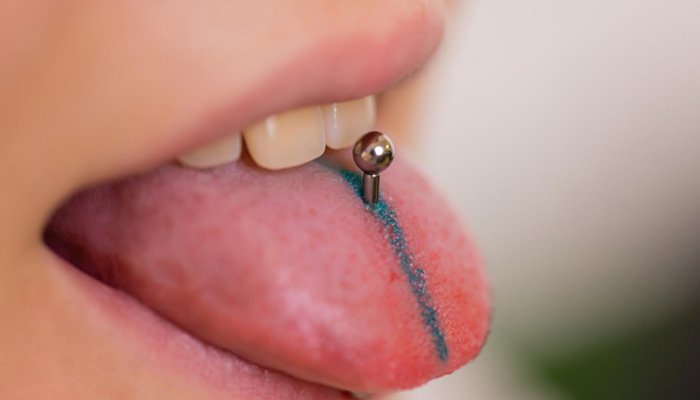
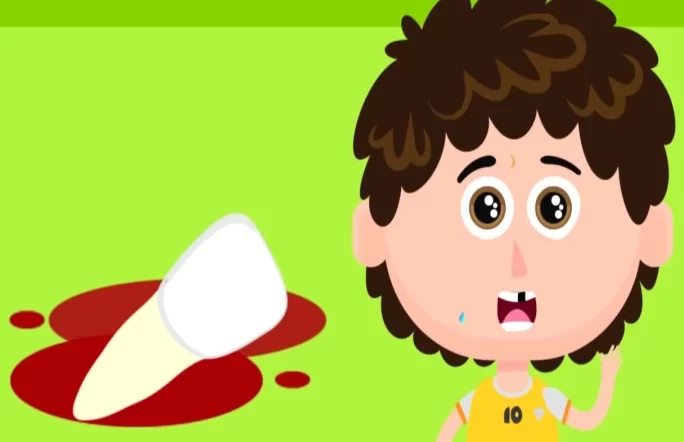
A cut or bitten tongue, lip, or cheek are some common oral injuries that can occur accidentally in children. This is due to the presence of thin layers of skin around the mouth. When a cut occurs on the tongue, cheek, or lips, they bleed excessively due to their rich blood supply. Attending to the bleeding and seeking medical care could be the best response in such situations.
Symptoms
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Swelling
- Redness
- Bruising
- Difficulty in eating and drinking
Necessary tips to follow at the time of injury
Clean the wound: Carefully wash the wound with clean water and remove any debris in the mouth. Rinse with salt water to prevent infection.
Bleeding: Apply pressure to the area of the wound with a gauze cloth till the bleeding stops, and then clean the wound.
Cold compression: Ice wrapped in a cloth can be applied to the wound to reduce pain and swelling, as can medications for pain relief.
Avoid certain drinks: Avoid cool, acidic, salty, and spicy foods, which make the wound worse. Take soft, liquid foods until the wound heals.
Monitor the wound: Check for any signs of infection, like unusual discharge like pus or a foul smell in your wound. If it does not heal within a week, consult a doctor.
Preventive measures
- Make sure your children do not chew hard objects such as pencils, pens, and fingernails that can cause cuts in their mouths.
- While playing sports, wear a helmet, facemask, and mouthguard to avoid injuries.
- Take the necessary steps to baby-proof households and protect children.
- Encourage your child to eat peacefully so that they can concentrate on their food.
- Make children chew slowly to avoid cuts to the tongue and lips.
- Try to avoid foods that have sharp edges.