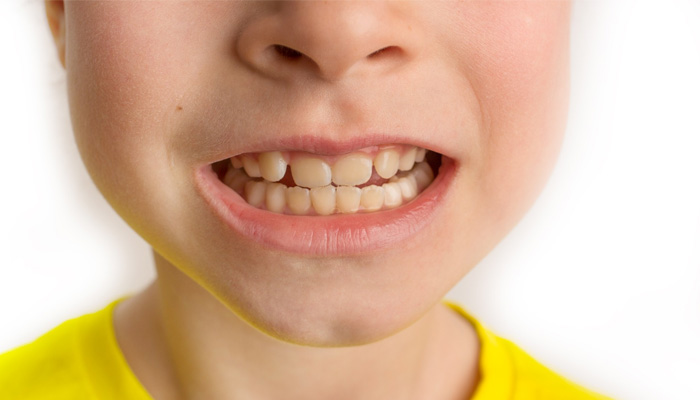
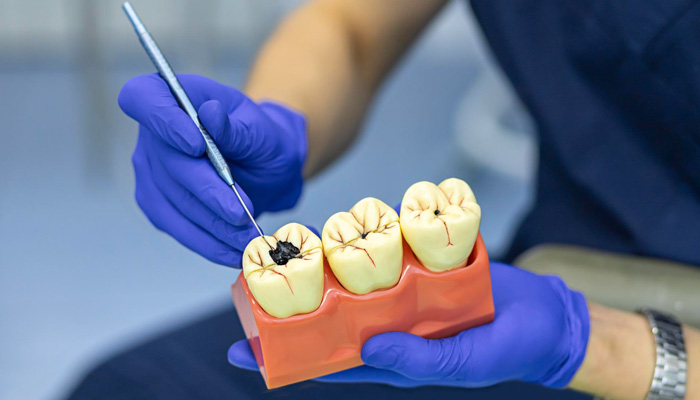
Rampant caries, also known as early Childhood Caries (ECC) and baby bottle tooth decay, is a severe form of tooth decay that affects young children, typically aged 0 to 5 years. It occurs when a child’s teeth are extensively decayed due to prolonged exposure to sugary substances, especially in bottles or sippy cups.
Causes of Rampant Caries:
- Frequent and prolonged exposure to sugary drinks: Giving a child sugary beverages like milk, formula, fruit juice, or sugary drinks in a bottle or sippy cup throughout the day or during bedtime can bathe the teeth in sugar for extended periods, promoting tooth decay.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of plaque, which contains bacteria that produce acids and damage the tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
- Sharing utensils or licking pacifiers: The transfer of saliva from caregivers or parents to the child can introduce harmful bacteria into the child’s mouth, increasing the risk of ECC.
- High-carbohydrate diets: Consuming a diet high in carbohydrates and sugary snacks can contribute to the development of ECC.
Symptoms of Rampant Caries:
Early Childhood Caries can manifest in various ways, including:
- White spots or lines on the teeth.
- Brown or black spots or holes (cavities) on the teeth.
- Tooth sensitivity or pain.
- Difficulty eating or chewing.
- Swelling or redness of the gums.
Prevention and Management:
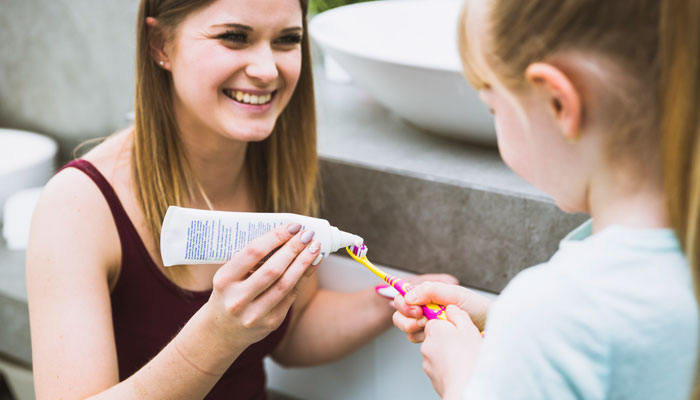
- Good oral hygiene: Clean your child’s mouth even before the first tooth erupts. Use a soft cloth or infant toothbrush to wipe their gums. Once teeth appear, use a small, soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste in an appropriate amount.
- Limit sugary beverages and snacks, especially between meals and before bedtime.
- Encourage sippy cup use: Transition from a bottle to a regular cup as early as possible, preferably by age one.
- Fluoride: Ensure your child receives an appropriate amount of fluoride, as it helps strengthen tooth enamel and prevents decay. This can be through drinking water or fluoride supplements if needed.
- Regular dental check-ups: Take your child for their first dental visit by their first birthday or shortly after the first tooth emerges. Regular dental check-ups help identify and address any oral health issues early.
- Dental sealants: Consider applying dental sealants on your child’s molars to protect them from decay.
If you suspect your child has Early Childhood Caries, seek the advice of a pediatric dentist for proper evaluation and treatment. Early intervention is essential to prevent the condition from worsening and affecting your child’s overall health and development.