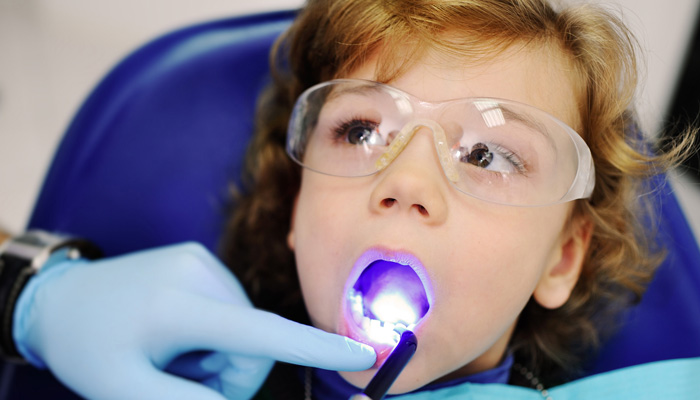
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) is a liquid solution used in pediatric dentistry to treat and prevent tooth decay, especially in milk teeth. It has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness, simplicity of use, and minimally invasive nature.
Here are some key points about Silver Diamine Fluoride and its use in pediatric dentistry:
What is SDF?
- SDF is a clear liquid solution composed of silver particles and fluoride. The silver component acts as an antimicrobial agent that helps to kill bacteria responsible for tooth decay, while the fluoride promotes remineralization, strengthening the tooth’s enamel.
Indications for Use:
- SDF is primarily used to arrest or stop the progression of tooth decay in primary teeth. It is particularly useful in young children who may have difficulty tolerating traditional dental treatments or in those with special needs who cannot cooperate fully in the dental chair.
Application Process:
- The application of SDF is simple and non-invasive. The dentist or dental professional will dry the affected tooth surface and apply the SDF liquid using a micro brush. The liquid is left to sit for a short period, and then the excess is rinsed off.
Advantages:
- It is a quick and painless procedure, making it suitable for children who may be fearful of traditional dental treatments. It is cost-effective and may avoid the need for more extensive restorative procedures, such as dental fillings.
Limitations:
- While SDF is effective at stopping the progression of decay, it does not restore the tooth’s structure. Dark staining may occur on the treated area, which can be a cosmetic concern, especially for front teeth. The staining is more noticeable on cavities and teeth with exposed dentin.
Patient Selection:
- SDF is best suited for certain patient populations such as
- young children,
- patients with early childhood caries (ECC),
- patients with special needs, or
- patients with significant dental anxiety.
Parental Consent:
- Before using SDF, dentists typically obtain informed consent from parents or guardians, explaining the benefits and limitations of the treatment, as well as any potential side effects.
Follow-up Care:
After SDF treatment, the dentist will monitor the treated teeth regularly to assess the stability of the lesion and decide if additional treatment or restoration is necessary.
Safety:
- SDF has been used for decades in other countries and has shown to be generally safe. However, it contains silver, so patients with known silver allergies should not receive SDF treatment.
It’s essential to consult a qualified pediatric dentist to determine if SDF treatment is suitable for a child’s specific dental needs and medical history. SDF can be a valuable tool in managing dental caries in pediatric patients, but it is just one of many options available to dentists in their efforts to protect children’s oral health.